People are forced to make choices because of:
a. unlimited wants and unlimited resources.
b. limited wants and unlimited resources.
c. unlimited wants and limited resources.
d. limited wants and limited resources.
e. irrational wants and limited resources.
c
You might also like to view...
Suppose a monopolist faces the demand curve shown below. 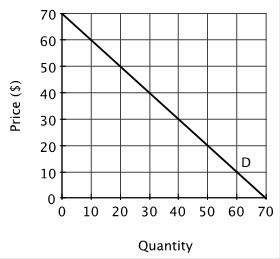 The monopolist maximizes its profits by:
The monopolist maximizes its profits by:
A. producing 35 units, since this is where total revenue is maximized. B. charging $70 for each unit. C. producing the level of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost. D. producing the level of output at which marginal revenue minus marginal cost is greatest.
Suppose Joe has a two-year old Honda Civic that's in excellent condition and that he would be willing to sell for $13,000. Lauren, who is risk-neutral, is considering whether to buy Joe's car. She's willing to pay $14,000 for a two-year Honda Civic that's in excellent condition and only $10,000 for one that's not in excellent condition. Lauren cannot tell whether Joe's car is in excellent condition. She believes that only 20 percent of two-year old Hondas for sale in the market are in excellent condition and that the other 80 percent are not in excellent condition. If other people who own two-year Honda Civics in excellent condition are like Joe, and other buyers in the market are like Lauren, then which of the following is likely to occur in the long run?
A. The sales price of two-year old Hondas will not change. B. The quality of two-year old Honda Civics offered for sale will rise. C. The sales price of two-year old Hondas will rise. D. The quality of two-year old Honda Civics offered for sale will fall.
For a monopolist
A. marginal revenue equals average revenue. B. marginal revenue is greater than price. C. marginal revenue equals price. D. marginal revenue is less than price.
The estimated price elasticities of demand for the products listed in the table as "Product A" are from Table 7-7 in the text. Indicate whether the products listed as "Product B" will have a more elastic or less elastic demand than the corresponding
Product A. Product A Estimated Elasticity for Product A Product B Is Estimated Elasticity for Product B More Elastic or Less Elastic than for Product A? Beer -0.29 Samuel Adams Boston Lager Chicken -0.37 Organically raised chicken Cocaine -0.28 Illegal narcotics Cigarettes -0.25 Marlboro Lights Restaurant meals -0.67 Denny's Grand Slam breakfast What will be an ideal response?