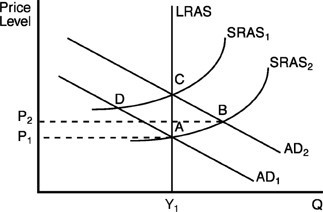
 In the above figure, if initial equilibrium is at point A and there is a fully anticipated increase in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 due to an anticipated increase in the money supply, then
In the above figure, if initial equilibrium is at point A and there is a fully anticipated increase in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 due to an anticipated increase in the money supply, then
A. the economy will move directly from point A to point B, and will remain at point B in the long run.
B. the price level will shift to P2 in the short run.
C. the economy will move directly from point A to point C without passing through point B.
D. the price level will shift to P2 in the long run.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Why does investment spending rise and fall with the overall level of GDP in the economy?
What will be an ideal response?
How do perfectly competitive markets allow for the movement of resources from less productive industries to more productive industries?
What will be an ideal response?
In the sequential labor negotiation game:
a. The ability to commit to a strategy gives you an advantage b. The ability to commit to a strategy gives your opponent an advantage c. The ability to commit to a strategy is irrelevant d. Players should simply state their desire to commit to a strategy to obtain an advantage
Reserves that banks are required by law to keep on hand to back up their deposits are called
a. required reserves. b. borrowed reserves. c. actual reserves. d. excess reserves.