After a price floor of $23 is placed on the market in the graph shown, which area represents consumer surplus?
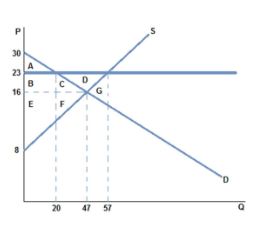
A. A
B. A + B
C. A + B + C
D. A + B + C + D
A. A
You might also like to view...
Refer to Goods X and Y. Suppose the consumer is spending all of his income buying some of both goods. If the marginal value of X is greater than the relative price of X, how can the consumer improve his level of satisfaction?
Assume that good X is on the horizontal axis and good Y is on the vertical axis in the consumer-choice diagram. PX denotes the price of good X, PY is the price of good Y, and I is the consumer's income. Unless otherwise stated, the consumer's preferences are assumed to satisfy the standard assumptions. a. By purchasing more of both goods. b. By purchasing more of good X and less of good Y. c. By purchasing more of good Y and less of good X. d. The consumer cannot improve his level of satisfaction because he is at the optimum.
In order to have an impact, a ________ must be set below the equilibrium price, and when this occurs, ________
A) price ceiling; consumer surplus increases B) price floor; consumer surplus decreases C) price ceiling; producer surplus decreases D) price support; total revenue increases E) price support; consumer surplus increases
Currently Belize, a country in Central America, has a small coffee industry but does not export any coffee
Suppose the government of Belize, in order to protect the new coffee industry to enable it to grow into a mature industry that can compete in world markets, places a tariff on the importation of coffee. What is the argument that has been used to support the tariff on coffee? A) the infant-industry argument B) the dumping argument C) protection of Belize coffee workers D) to prevent rich countries from exploiting developing countries
Permits that allow a firm to emit a specific amount of pollution are called ____________
a. Pigouvian or pollution taxes b. tradable pollution permits c. pollution standards d. technology-based regulations e. None of the above.