Figure 10-2
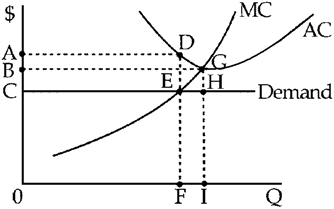
Figure 10-2 shows demand and short-run cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. In the short run, this firm would
a.
earn positive economic profits.
b.
earn economic losses.
c.
go out of business.
d.
Cannot be determined with the information given.
b
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.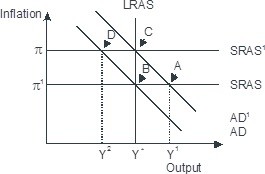
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary
A monopolist charges $7 per unit for selling 6 units of his product. To sell 7 units, he reduces price to $6.5 per unit. The marginal revenue (net addition to revenue) from selling the seventh unit is then $3.5
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The largest single expenditure component of GDP is: a. consumption
b. investment. c. government purchases. d. net exports.
Will is risk averse and has $1,000 with which to make a financial investment. He has three options. Option A is a risk-free government bond that pays 5 percent interest each year for two years. Option B is a low-risk stock that analysts expect to be worth about $1,102.50 in two years. Option C is a high-risk stock that is expected to be worth about $1,200 in four years. Will should choose
a. option A. b. option B. c. option C. d. either option A or option B because Will is indifferent between those two options and they are superior to option C.