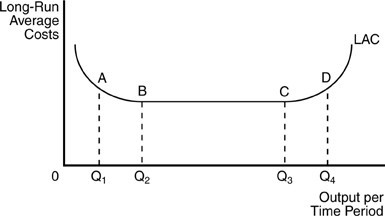
 In the above figure, for any output level less than Q2, this firm experiences
In the above figure, for any output level less than Q2, this firm experiences
A. decreasing long run average costs.
B. diseconomies of scale.
C. constant economies of scale.
D. economies of scale.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Firm A is a monopoly. The demand for its output is p = 90 - Q. Production is such that Q = L. Firm A hires only unionized labor. The marginal cost to the union is $10 per unit of labor. The union will sell
A) 20 units of labor at a wage of $10. B) 20 units of labor at a wage of $40. C) 20 units of labor at a wage of $50. D) 20 units of labor at a wage of $70.
Suppose two firms are in a game situation, and they each must decide on a strategy regarding whether to select a high price or a low price Profits for a firm are highest when it selects a low price, while the other selects a high price; profits are lowest if one selects a high price, while the other selects a low price; profits are in between when both select low prices; and profits are slightly higher when both select high prices. In the absence of collusion we expect
A) one of the firms to select a high price and the other a low price. B) one firm to select a high price and the other a low price in the first period, followed by a reversal in the second period. C) both to select high prices. D) both to select low prices.
Assume that the central bank lowers the discount to increase the nation's monetary base. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the real GDP and the monetary base in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? State your answer after the macroeconomic system returns to complete equilibrium
a. Real GDP rises and monetary base rises. b. Real GDP rises and monetary base falls. c. Real GDP and monetary base fall. d. Real GDP and monetary base remain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
The return on the money risked on a share of stock is called
A. retained earnings. B. interest. C. capital gains. D. dividends.