The trilemma refers to all the following EXCEPT:
a. a fixed exchange rate.
b. international capital mobility.
c. monetary policy autonomy.
d. price controls.
Ans: d. price controls.
You might also like to view...
________ occurs when one party takes advantage of having more information than another party about the attributes of the good or service they will exchange
A) A negative externality B) Adverse selection C) A transaction cost D) Moral hazard
The law of increasing opportunity cost means that:
A) higher wages, rents, and interest will increase opportunity costs. B) opportunity cost will decrease the more you decide to produce more of one good along a production possibilities curve. C) opportunity cost increases when you produce more of one good while moving along a production possibilities curve. D) costs of production decrease at first, but then eventually rise.
You are planning to open a new Italian restaurant in your hometown where there are three other Italian restaurants. You plan to distinguish your restaurant from your competitors by offering northern Italian cuisine and using locally grown organic
produce. What is likely to happen in the restaurant market in your hometown after you open? A) Your competitors are likely to change their menus to make their products more similar to yours. B) The demand curve facing each restaurant owner shifts to the right. C) The demand curve facing each restaurant owner becomes more elastic. D) While the demand curves facing your competitors becomes more elastic, your demand curve will be inelastic.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 29.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.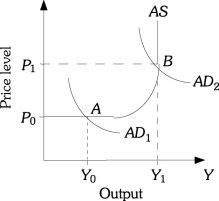 Figure 29.2Refer to Figure 29.2. If the economy is currently at Point A and policy makers implement a policy to increase aggregate demand, the time the economy needs to make the adjustment is known as the
Figure 29.2Refer to Figure 29.2. If the economy is currently at Point A and policy makers implement a policy to increase aggregate demand, the time the economy needs to make the adjustment is known as the
A. frictional lag. B. response lag. C. implementation lag. D. recognition lag.