Part of the explanation for why the aggregate-demand curve slopes downward is that a decrease in the price level
a. decreases the real value of money.
b. increases the real value of the dollar in foreign exchange markets.
c. decreases the interest rate.
d. All of the above are correct.
c
You might also like to view...
If you put $500 into a checking account, the immediate effect (do not consider the money multiplier which we will study in the next chapter) is:
a. M1 rises, M2 falls, and the monetary base remains the same. b. M1 falls, M2 falls, and the monetary base remains the same. c. M1 rises, M2 rises, and the monetary base remains the same. d. M1, M2, and the monetary base fall. e. M1, M2, and the monetary base remain the same.
Which of the following would those in favor of increasing government spending rather than decreasing taxes to prop up aggregate demand probably not agree with?
a. Traditional Keynesian analysis indicates that increases in government purchases are a more potent tool than decreases in taxes for increasing aggregate demand. b. Increased government spending on "shovel-ready" projects can be helpful to boost aggregate demand. c. Increases in government spending offer a greater "bang for the buck" than decreases in taxes. d. When the government gives a dollar in tax cuts to a household, that dollar immediately and fully adds to aggregate demand.
Figure 3-18
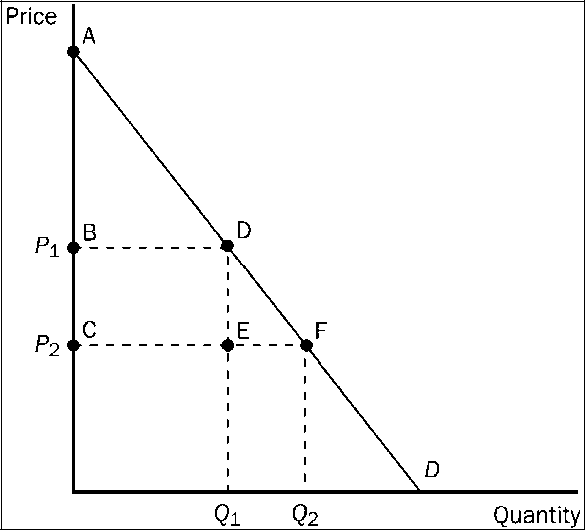
Refer to . When the price falls from P1 to P2, which area represents the increase in consumer surplus to new buyers entering the market?
a.
ABD
b.
ACF
c.
BCDE
d.
DEF
The inflationary gap is the
A. inflation rate that will occur from excess aggregate demand. B. budget deficit that caused the inflation to occur. C. distance between the equilibrium level of output and the full employment level of output. D. gap between expected and actual inflation.