Consider the cooling of (a) a personal computer with a separate CPU, and (b) a laptop computer. The reliable functioning of these machines depends upon their effective cooling. Identify and briefly explain all modes of heat transfer that are involved in the cooling process.
GIVEN
- A personal computer with a separate CPU (the monitor, keyboard, and mouse are separate and not
considered).
- A laptop computer.
FIND
Identify and describe modes of heat transfer involved in their cooling.
ASSUMPTIONS
- The computers are turned on and in normal operation.
(a) The cooling would first involve conduction from microchips to heat sinks (finned structures)
mounted on them as well as conduction to the surface of printed-circuit boards, and convection
from heat sinks and printed-circuit boards to air flowing over them (most PCs have a fan that
blows air through the computer compartment). From the printed circuit boards, which are
mounted to the casing of the computer, heat would also be conducted to the casing. Furthermore,
there would be some radiation from heat sinks and printed-circuit boards to the casing, and then
from outer computer casing to the surroundings; from the outer casing there will also be
convection (natural convection) heat loss to the room’s atmosphere.
(b) In a laptop computer, the heat produced in the microchips and other electrical circuitry would be
conducted to the heat sinks mounted on them as well as through the circuit boards to the casing of
the computer. From the outer casing the heat would then be dissipated by natural convection and
radiation to the room’s atmosphere. Some laptop computers come mounted with a small fan, in
which case heat removal by internal forced convection would also be part of the total thermal
management (cooling strategy) of the device. Furthermore, some makers install heat pipes in the
casing for heat removal. A heat pipe is a “wicking” device that involves evaporation of a thin
liquid film inside the device and the condensation of vapor so generated (the student can learn
more about a heat pipe
You might also like to view...
A 2.00 kg mass is moving in a circular path with a radius of 5.00 cm. The mass starts from rest and with constant angular acceleration, obtains an angular velocity of 6.00 rad/sec in 3.00 sec. The mass then comes to a stop with constant deceleration in 4.00 sec. The centripetal component of acceleration of the mass at 2.00 sec is
A. 1.220 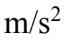
B. 0.980 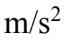
C. 0.806 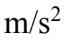
D. 0.656 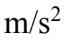
E. 0.520 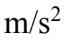
The speed of sound through the ground is about 6.0 km/s while the speed of sound in air is 343 m/s. A very powerful explosion occurs some distance away and you feel the ground vibrate 60 seconds before you hear the sound of the explosion
How far away is the explosion? A) 20 km B) 22 km C) 25 km D) 27 km E) 30 km
The sky is the deepest blue
A) just before a rainstorm. B) during a rainstorm. C) just after a rainstorm. D) when the air is humid. E) just before sunset.
Fresh water enters the ocean by runoff from streams and rivers,
A) precipitation of rain over the ocean, and evaporation of coastal waters. B) evaporation of surface water, and melting of glacial ice. C) precipitation, and melting of glacial ice. D) none of these