The image of an object beneath the surface of a medium of refractive index n> 1 is seen in air by a person looking down on the surface. This image, formed by light rays leaving the flat refractive surface, is
A. real and closer to the viewer than the object.
B. virtual and closer to the viewer than the object.
C. real and farther from the viewer than the object.
D. virtual and farther from the viewer than the object.
E. virtual and the same distance from the viewer as the object.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The equation that solves a problem is 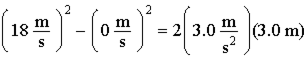
A. What is the initial velocity of a car that goes from rest to 18 m/s in 3.0 s? B. What is the final velocity of a car that goes from rest to 18 m/s in 3.0 s? C. What is the initial velocity of a car that accelerates at 18 m/s for 3.0 s? D. What is the final velocity of a car that accelerates at 3.0 m/s2 over a 6.0 m distance? E. What is the final velocity of a car that accelerates at 3.0 m/s2 over a 3.0 m distance?
A gravitational lens occurs when
A) a massive object causes more distant objects to appear much larger than they should, and we can observe the distant objects with better resolution. B) a telescope lens is distorted by gravity. C) a massive object bends light beams that are passing nearby. D) dark matter builds up in a particular region of space, leading to a very dense region and an extremely high mass-to-light ratio.
Two flat 4.0 cm × 4.0 cm electrodes carrying equal but opposite charges are spaced 2.0 mm apart with their midpoints opposite each other
Between the electrodes but not near their edges, the electric field strength is 2.5 × 106 N/C. What is the magnitude of the charge on each electrode? (?0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N • m2) A) 35 nC B) 18 nC C) 16 nC D) 30 nC
About the Intermediate Physics category
Explore Intermediate Physics homework help here