A large stone is resting on the bottom of the swimming pool. The normal force of the bottom of the pool on the stone is equal to the
a. weight of the stone.
b. weight of the water displaced.
c. sum of the weight of the stone and the weight of the displaced water.
d. difference between the weight of the stone and the weight of the displaced water.
d
You might also like to view...
Addition by 1. Components: Three forces, 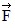 1,
1, 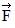 2, and
2, and 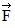 3, all act on an object, as shown in the figure. The magnitudes of the forces are: F1 = 80.0 N, F2 = 60.0 N, and F3 = 40.0 N. The resultant force acting on the object is given by
3, all act on an object, as shown in the figure. The magnitudes of the forces are: F1 = 80.0 N, F2 = 60.0 N, and F3 = 40.0 N. The resultant force acting on the object is given by 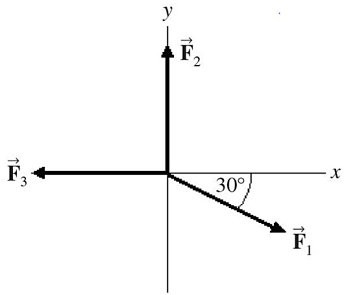
A. 180 N at an angle of 60.0° with respect to +x-axis. B. 60.0 N at an angle of 90.0° with respect to +x-axis. C. 20.0 N at an angle of 34.3° with respect to +x-axis. D. 35.5 N at an angle of 34.3° with respect to +x-axis. E. 40.0 N at an angle of 60.0° with respect to +x-axis.
Process of Science: We cannot test the nebular theory for the formation of the Solar System in a rigorous scientific way because the Sun and planets formed in the distant past
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
A researcher is investigating a cubic crystal with x rays. He is looking at Bragg reflection from the planes parallel to the cube faces
He finds that when using x rays of 0.165 nm a strong first maximum occurs when the beam makes an angle of 23.5° with the planes. What is the spacing of adjacent atoms in the crystal?
How can interstellar dust block starlight in spite of its extremely low density?
What will be an ideal response?