A move from F to G represents a
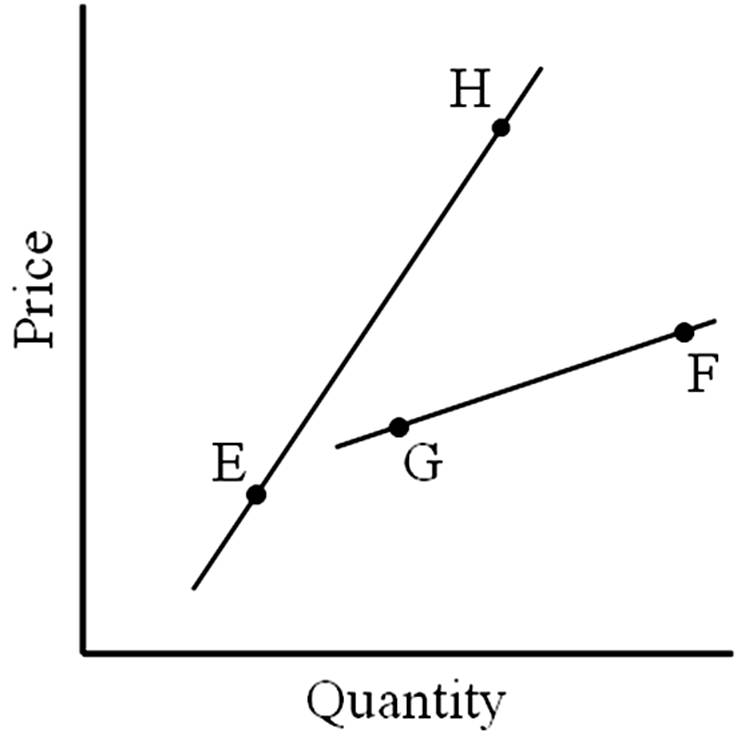
A. change in quantity supplied.
B. change in supply.
C. increase in supply.
D. decrease in supply.
A. change in quantity supplied.
You might also like to view...
Lucas argues that when policies change, expectations will change thereby
A) changing the relationships in econometric models. B) causing the government to abandon its discretionary stance. C) forcing the Fed to keep its deliberations secret. D) making it easier to predict the effects of policy changes.
Refer to the above figure. A long-run equilibrium in monopolistic competition is pictured by
A) Panel A. B) Panel B. C) Panel C. D) Panel D.
Bill can cook dinner in 45 minutes and mow the lawn in 1.5 hours. Eileen can cook dinner in 1.5 hours and mow the lawn in 2 hours. Bill's opportunity cost of mowing the lawn is
a. 1/2 of a dinner b. 2 dinners c. 3/4 of a dinner d. 1-1/3 dinners e. 2-2/3 dinners
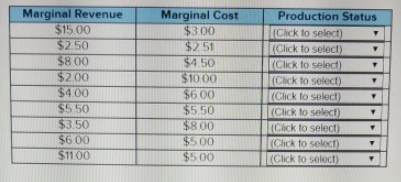
State whether each condition is consistent with profit maximization or if production should increase or decrease.