Refer to Common Property I. If access to the common property cannot be prohibited, then the resulting social gain equals
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the benefits and costs associated with the use of a common property.
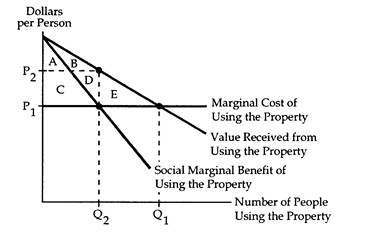
a. zero.
b. area E.
c. area A + B.
d. area C + D.
a. zero.
You might also like to view...
Nick owns a dog whose barking annoys his neighbor Jane. Suppose that the benefit of owning the dog is worth $500 to Nick, and that Jane bears a cost of $700 from the barking. Assume that the city has no ordinance against barking dogs. A possible private solution that would benefit both parties is for: a. Jane to pay Nick $450 to get rid of the dog
b. Nick to pay Jane $650 for her inconvenience. c. Jane to pay Nick $650 to get rid of the dog. d. There is no private solution that would improve this situation for both parties.
If net taxes are cut, consumer
a. spending is not affected b. spending increases by the amount of the tax cut c. spending increases by an amount less than the full amount of the tax cut d. saving increases by the full amount of the tax cut e. spending increases by two-thirds of the amount of the tax cut and consumer saving increases by one-third of the amount of the tax cut
If a positive permanent supply shock were to occur, the resulting equilibrium would be a:
A. higher level of output at lower prices. B. lower level of output and prices. C. higher level of output and prices. D. lower level of output at higher prices.
Vertical differentiation makes products better for some consumers and worse for others.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)