The output losses from an adverse inflation shock are ________ and the output losses from a fall in potential output are ________.
A. large; small
B. small; large
C. permanent; temporary
D. temporary; permanent
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Suppose the equilibrium price of oranges is $2.00 per pound. If the actual price is above the equilibrium price, a
A) shortage exists and the price falls to restore equilibrium. B) shortage exists and the price rises to restore equilibrium. C) surplus exists and the price falls to restore equilibrium. D) surplus exists and the price rises to restore equilibrium. E) surplus exists but nothing happens until either the demand or the supply changes.
Large manufacturing firms that buy many different parts or components (e.g., auto manufacturers) can choose which parts to buy from other firms and which parts to make in their own factories
These manufacturers may be able to use monopsony power to reduce the price paid to outside suppliers for parts that are: A) standard components for many manufacturers so that there are many buyers and sellers. B) only used in their cars so that there is one buyer and a few sellers. C) bought and sold in perfectly competitive markets. D) none of the above
The last federal budget surplus was in which of these years?
A. 1983-1985 B. 1975-1980 C. 1998-2000 D. 1991-1996
Refer to the information provided in Table 20.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 20.3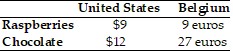 Refer to Table 20.3. If the exchange rate is $1 = 3 euros, then
Refer to Table 20.3. If the exchange rate is $1 = 3 euros, then
A. Belgium will import both raspberries and chocolate. B. the United States will import raspberries and Belgium will import chocolate. C. the United States will import chocolate and Belgium will import raspberries. D. the United States will import both raspberries and chocolate.