The explosion of a supernova type II can leave behind
a. a planetary nebula.
b. a shell of hot, expanding gas with a white dwarf at the center.
c. a shell of hot, expanding gas with a neutron star at the center.
d. Nothing is ever left behind.
c
You might also like to view...
The longitudinal strength of wood is due to the high strength of crystalline _________cells.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
An ideal heat engine can have an efficiency of 1 if the temperature of the low temperature reservoir is
a. 0 K. b. 0°C. c. 0°F. d. 0°R. e. the same as the temperature of the heat source.
Red dwarf stars ____
a. never develop a hydrogen-fusion shell b. create large amounts of carbon and oxygen c. have much shorter lifetimes than Sun-like stars d. never begin hydrogen fusion e. become brown dwarfs after they exhaust their hydrogen core
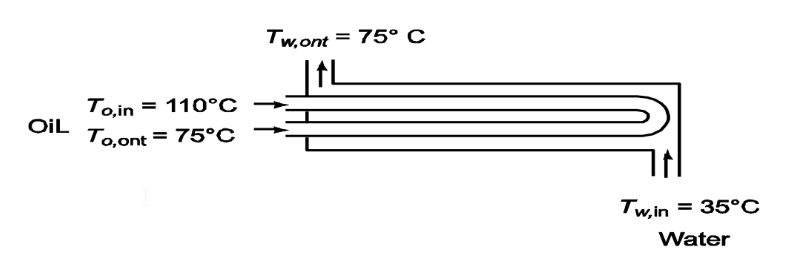
Water entering a shell-and-tube heat exchanger at 35°C is to be heated to 75°C by an oil. The oil enters at 110°C and leaves at 75°C. The heat exchanger is arranged for counterflow with the water making one shell pass and the oil two tube passes. If the water flow rate is 68 kg per minute and the overall heat transfer coefficient is estimated from Table 10.1 to be 320 W/(m2 K), calculate the required heat exchanger area.
GIVEN
• One shell pass, two tube passes counterflow heat exchanger with water in shell, oil in tube
• Water temperatures Tw,in = 35°C Tw,out = 75°C
• Oil temperatures To,in = 110°C Tw,out = 75°C
• Water flow rate m n= 68 kg/min = 1.133 kg/s
• Overall heat transfer coefficient (U) = 320 W/(m2 K)
FIND
• The required area (A)
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the specific heat of water at the average temperature of 55°C (cpw)= 4180 J/(kg K)