Refer to the cost table below. If a competitive firm faced with these costs finds that it can sell its product at $60 per unit, it will:
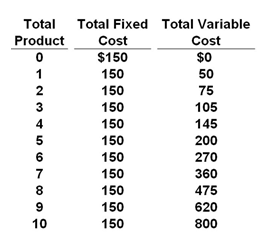
A. Produce 5 units and incur a loss of $50
B. Produce 6 units and incur a loss of $30
C. Produce 7 units and realize a profit of $32
D. Close down in the short run
A. Produce 5 units and incur a loss of $50
You might also like to view...
An unpaid worker in a family business is classified as
A) not in the labor force. B) employed no matter how many hours the person worked in the previous week. C) unemployed no matter how many hours the person worked in the previous week. D) employed if the person worked at least 15 hours in the previous week. E) unemployed only if the person worked no hours in the previous week.
Why does an external cost lead to inefficient overproduction?
What will be an ideal response?
Money as a medium of exchange I. Facilitates the exchange of goods II. Reduces the incentive to barter
A. I only B. II only C. Both I and II D. Neither I nor II
Exhibit 10-12 Income distribution for three countries QuintileCountry I (%) Country II (%) Country III (%) Poorest 6 8 4 Second12 12 8 Third15 15 10 Fourth27 30 30 Richest40 35 48 Exhibit 10-12 shows the percentage of income received by each population quintile. In Country I we can conclude that the:
A. richest 20 percent of the population received 25 percent of the economy's income. B. richest 20 percent of the population received 40 percent of the economy's income. C. richest 20 percent of the population received 80 percent of the economy's income. D. least-wealthy 20 percent of the population received 40 percent of the economy's income.