Explain the essential difference between fixed and flexible exchange rate systems
Fixed exchange rates involve an official act by government officials to fix and peg its currency to all other
currencies. This means that the government must stand ready to buy or sell its own currency in exchange
for foreign currencies. Flexible exchange rates are established by the free interaction of demand and supply.
The government has no role to play in establishing the exchange rate between its currency and that of any
other nation. Exchange rates appreciate and depreciate entirely in accordance with free market forces.
You might also like to view...
Pricing insurance policies is made difficult because buyers have more information than sellers. This difficulty is an example of
A) adverse selection. B) asymmetric information. C) the free-rider problem. D) moral hazard.
Suppose that a worker in Freedonia can produce either 6 units of corn or 2 units of wheat per year, and a worker in Sylvania can produce either 2 units of corn or 6 units of wheat per year. Each nation has 10 workers. Without trade, Freedonia produces and consumes 30 units of corn and 10 units of wheat per year. Sylvania produces and consumes 10 units of corn and 30 units of wheat. Suppose that trade is then initiated between the two countries, and Freedonia sends 30 units of corn to Sylvania in exchange for 30 units of wheat. Freedonia will now be able to consume a maximum of
a. 30 units of corn and 30 units of wheat. b. 40 units of corn and 30 units of wheat. c. 40 units of corn and 20 units of wheat. d. 10 units of corn and 40 units of wheat.
Based on the table showing poverty for different groups, the group with the highest poverty rate is ______.
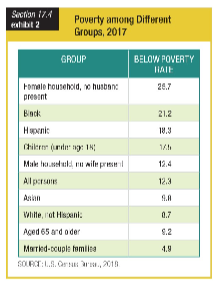
a. female households with no husband present
b. male households with no wife present
c. white, non-Hispanics
d. over 65 years old
"An oligopoly is an oligopoly. Firms behave the same no matter what type of oligopoly it is." This statement is true of:
A. Cournot and Stackelberg oligopolies. B. Bertrand and Stackelberg oligopolies. C. Bertrand and Cournot oligopolies. D. None of the answers is correct.