Wages are the major element of cost in the economy accounting for about 70 percent of all input costs.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
True
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1 A farmer has a comparative advantage at growing wheat if his cost of growing wheat is smaller than his cost of growing any other crop. 2. A farmer has a comparative advantage at growing wheat if his cost of growing wheat is less than the cost of another farmer growing wheat. 3. By definition, someone who has an absolute advantage must also have a comparative advantage. 4. If there are only two activities on which a person can work, and there are two people to do the work, then it is impossible for one person to have a comparative advantage in both activities. 5. By definition, someone who has a comparative advantage in producing soft drinks must also have an absolute advantage in producing soft drinks.
The price paid to purchase land
A) has no relation to cost because it did not cost anything to produce the land. B) rarely has any relation to cost because it has usually been determined by competitive bidding. C) usually depends on the cost to the seller of letting the purchaser have the land. D) would more accurately reflect the social value of the land if the price were zero.
Suppose the current situation is such that the price level is 120, real GDP is $17 trillion, and GDP along the long-run aggregate supply curve is $16.6 trillion. What will take place to restore the long-run equilibrium?
A) The price level will fall until long-run aggregate supply increases to $17 trillion. B) The price level will fall and money wage rates will rise until real GDP along the long-run aggregate supply curve is $17 trillion. C) Money wage rates will rise until real GDP reaches $16.6 trillion. D) Aggregate demand will increase until both short-run and long-run aggregate supply equal $17 trillion.
These are the cost and revenue curves associated with a monopolistically competitive firm.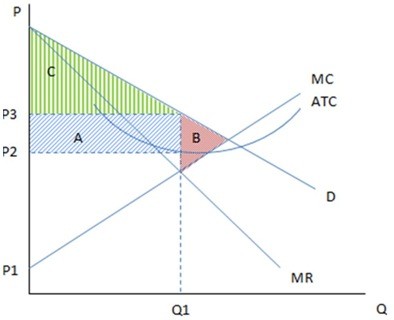 According to the graph shown, the monopolistically competitive firm will charge a price:
According to the graph shown, the monopolistically competitive firm will charge a price:
A. P3 in the long run, and earn zero profits. B. P2 in the short run, and earn positive profits. C. P2 in the long run, and earn zero profits. D. P3 in the short run, and earn positive profits.