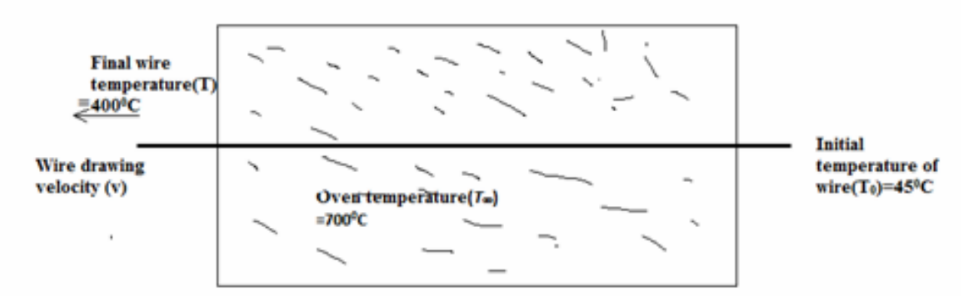
In a metal wire manufacturing facility, continuously drawn copper wire with a 2.5 mm diameter is annealed by heating it from its initial temperature of 450C to 400oC in a soaking oven. The oven inside air temperature is 7000C with an average heat transfer coefficient of ch =45 W/(m2 K). Estimate the soaking annealing time required. Also if the oven is 3.5 m long and the drawn wire is continuously fed through the oven (entering at one end and pulled out at the other longitudinal end), what should be the drawing speed or velocity?
GIVEN
• Copper wire with diameter (D)= 2.5 mm=0.0025 m
• Initial temperature of the wire(To) = 45°C
• Oven air temperature(T?) = 700°C
• Heat transfer coefficient ( ch ) = 45 W/(m2 K)
• Length of the oven(L)=3.5 m
FIND
• The soaking annealing time required for the wire to 400°C
• Drawing speed through the oven(v)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Constant thermal conductivity
• End effects are negligible
• The wire is very long compared to its diameter
• There is radial conduction only in the wire
SKETCH
(a) The Biot number is calculated first to check if the internal resistance is negligible
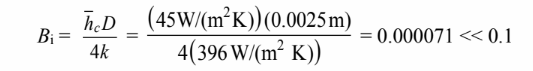
Therefore, the internal resistance of the rod is negligible.
The temperature-time history of the rod,
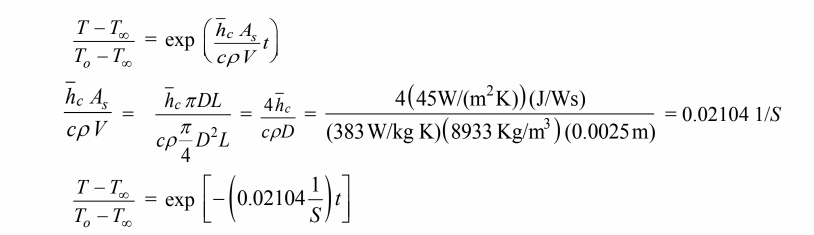
Solving for the time
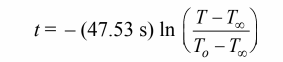
The time required to reach 88°C is

(b) Drawing speed through oven
Length of the oven(L)=3.5 m
Time required for soaking annealing to 4000C(t)=37 seconds
Thus drawing speed(v)=L/t= 3.5 m/37 s=0.095 m/s =9.5 cm/s
You might also like to view...
What evidence do we have that Earth has a molten core?
What will be an ideal response?
Thin Lenses: A 4.0-cm-tall object is placed 50.0 cm from a diverging lens having a focal length of magnitude 25.0 cm. What is the nature and location of the image?
A. A real image, 4.0 cm tall, 20 cm other side of the object B. A virtual image, 4.0 cm tall, 20 cm other side of the object C. A virtual image, 2.0 cm tall, 10 cm other side of the object D. A virtual image, 1.3 cm tall, 16.7 cm same side as the object E. A real image, 1.3 cm tall, 16.7 cm same side as the object
An object slides on a level floor. It slows and comes to a stop with a constant acceleration of magnitude 2.4 m/s2. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the object and the floor?
A) 0.24 B) 0.48 C) 0.12 D) It is impossible to determine without knowing the mass of the object.
In a steam engine, steam at 140°C in a turbine does work on an external system, and the steam leaves the turbine at 100°C. The efficiency of the steam engine is 5%. The relevant physical principle is
a. the first law of thermodynamics b. the second law of thermodynamics c. specific heat capacity d. operation of a heat pump e. none of the above