Interest-rate ceilings on deposits:
a. meant banks were guaranteed "cheap money" from depositors
b. were imposed because without them, as was the case in the 1970s, banks couldn't be profitable.
c. led to banks losing deposits whenever market rates went above the ceiling rates.
d. are only effective when market rates are below the ceiling rates.
e. were developed by money market mutual funds as a marketing device.
c
You might also like to view...
The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines, A and B, of serving a particular route
If the two airlines must decide simultaneously, and the government imposes a $20 per firm tax on firms that service this route, which of the following maximizes the firms' joint profits? A) Neither firm services the route. B) Firm A offers firm B $20 to not enter. C) Both firms will service this route. D) Firm B offers firm A $30 to not enter.
As it relates to the R&D decision, the interest-rate cost-of-funds curve:
A. usually slopes downward. B. is the marginal cost element in the MB = MC decision framework. C. indicates a constant rate of return, r. D. reflects the interest rate on bank loans but not the implicit interest rate on the use of retained earnings.
The greater is the risk of non-repayment of a loan, the
A. longer is the expected time to repay the loan. B. lower is the expected rate of interest. C. higher is the expected rate of interest. D. lower is the handling charges for the loan.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.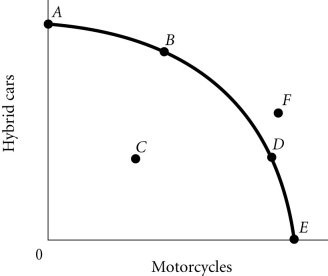 Figure 2.4Refer to Figure 2.4. The economy moves from Point A to Point D. This could be explained by
Figure 2.4Refer to Figure 2.4. The economy moves from Point A to Point D. This could be explained by
A. an increase in economic growth. B. a change in society's preferences for motorcycles versus hybrid cars. C. a reduction in unemployment. D. an improvement in technology.