The uneven distribution of an impermeable solute on either side of a membrane will result in
A. an increase in oxygen deprivation.
B. proton pumping.
C. root pressure.
D. osmosis.
E. stomatal closing.
D. osmosis.
The side of the membrane with the most solute would be hypertonic relative to the other side. This means water would flow via osmosis towards the side with the most solute.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following damaged templates encountered by a replication fork is repaired by double-strand break repair?
A. The replication fork encounters a lesion and translesion synthesis occurs. B. The replication fork encounters a lesion and stalls. C. The replication fork encounters a lesion and bypasses it, restarting synthesis on the other side of the lesion. D. The replication fork encounters a lesion at which repair has been initiated and the fork collapses. E. The replication fork encounters heteroduplex DNA.
Refer to Figure 14-1. The area of the tryptophan operon labeled 3 is the:
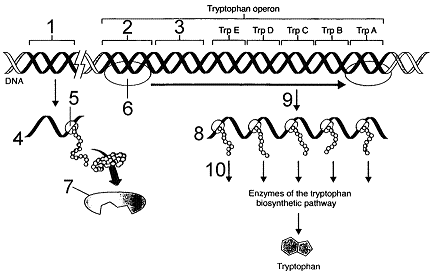
a. promoter.
b. repressor gene.
c. ribosome.
d. RNA polymerase.
e. operator
The actual physiological mechanism that allows fish to school involves both the cutaneous receptors known as the lateral line as well as their eyesight. Therefore, the stimuli that fish use to school are light and
A. molecules for taste. B. temperature. C. gravitational pull. D. pressure waves. E. sound waves.
First line of defense may be described as
A) the release of prostaglandins and leukotrienes in response to microbes. B) intact skin, mucous membranes, sebum, tears, and so forth. C) damage resulting in cell lysis. D) the coating of a pathogen by complement. E) nonspecific leukocytes that secrete toxins onto the surface of virally infected cells.