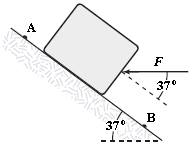
A 4.0-kg block is lowered down a 37° incline a distance of 5.0 m from point A to point B. A horizontal force (F = 10 N) is applied to the block between A and B as shown in the figure. The kinetic energy of the block at A is 10 J and at B it is 20 J. How much work is done on the block by the force of friction between A and B?
a.
?58 J
b.
?53 J
c.
?68 J
d.
?63 J
e.
?47 J
c
You might also like to view...
Regarding the charges of the electron, proton and neutron:
A) these objects are charged only when they reside in an ionized atom; otherwise, all three are uncharged. B) the proton has a positive charge, the electron has a much smaller negative charge, and the neutron has no charge. C) the proton has a positive charge, the neutron has a negative charge whose strength is equal to that of the proton's charge, and the electron has no charge. D) the electron has a negative charge, the proton has a positive charge, and the neutron has a charge that can be positive or negative or zero depending on the ionization of the atom in which it resides. E) the proton has a positive charge, the electron has a negative charge whose strength is equal to the strength of the proton's charge, and the neutron has no charge.
The noble gases, listed by increasing molecular weight, are He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Rn. If samples of 1 mole each of these gases are placed in separate containers and heated to 300 K, which gas has the greatest internal energy and the molecules of which gas have the highest rms speed?
a. The He has the greatest internal energy, and the Rn has the greatest rms speed. b. The Rn has the greatest internal energy, and the He has the greatest rms speed. c. All the gases have the same internal energy, and the Rn has the greatest rms speed. d. All the gases have the same internal energy, and the He has the greatest rms speed.
When the reflection of an object is seen in a concave mirror the image:
a. will always be enlarged. c. will always be virtual. b. may be either real or virtual. d. will always be real.
Which of the following played the most important role in the ring's formation?
A) Saturn's differential rotation B) Saturn's Roche limit C) Saturn's distance from the Sun D) debris from volcanoes on Mimas E) tidal resonance with Titan