The marginal tax rate is equal to the
A) total amount of a person's tax payment divided by the total amount of the person's taxable income.
B) total amount of a person's tax payment divided by the change in the person's taxable income.
C) change in the person's tax payment divided by the total amount of the person's taxable income.
D) change in the person's tax payment divided by the change in the person's taxable income.
D
You might also like to view...
The table below shows the weekly demand for hamburgers in a market where there are just three buyers.PriceQuantity Demanded by Buyer 1Quantity Demanded by Buyer 2Quantity Demanded by Buyer 3$6746597841510123211516Refer to the table. If there were 100 buyers in the market, each with a demand schedule identical to Buyer 3 in the table, then the weekly quantity of hamburgers demanded in the market at a price of $6 would be
A. 800. B. 700. C. 600. D. 400.
The definition of gross domestic product is
A. the total value of all sales in the economy. B. the total value of production in the domestic economy plus the production of domestic firms in foreign countries. C. the total value of all sales of final and intermediate goods in the domestic economy. D. the total of the money values of all final goods and services produced in the domestic economy within a specific time period.
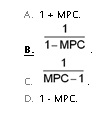
The formula for the multiplier is
The law of diminishing marginal returns
A. causes average fixed costs to decline continuously as output increases. B. causes the difference between average total cost and average variable cost to shrink as output increases. C. results in MC but not ATC curves eventually increasing at an increasing rate. D. results in average variable cost (AVC), average total cost (ATC), and marginal cost (MC) curves eventually increasing at an increasing rate.