Evaporation cools the liquid that is left behind because the molecules that leave the liquid during evaporation
a. have kinetic energy.
b. have greater than average speed.
c. have broken the bonds that held them in the liquid.
d. create vapor pressure.
b
You might also like to view...
Replot the data points of Figure 5.9(b) on log-log paper and find an equation approximating the best correlation line. Compare your results with Figure 5.10. Then, suppose that steam at 1 atm and 100°C is flowing across a 5-cm-OD pipe at a velocity of 1 m/s. Using the data in Figure 5.10, estimate the Nusselt number, the heat transfer coefficient, and the rate of heat transfer per meter length of pipe if the pipe is at 200°C and compare with predictions from your correlation equation.
GIVEN
Figure 5.9(b) in text
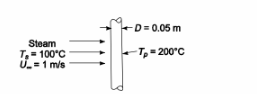
Steam flowing across a pipe
Steam pressure = 1 atm
Steam temperature (Ts) = 100°C
Pipe outside diameter (D) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Steam velocity (U?) = 1 m/s
Pipe temperature (Tp) = 200°C
FIND
(a) Replot Figure 5.9(b) on log-log paper and find an equation approximating the best correlation line
(b) Find the Nusselt number (Nu), the heat transfer coefficient (hc), and the rate of heat transfer per
unit length (q/L) using Figure 5.10
(c) Compare results with your correlated equation
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Radiative heat transfer is negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
From Appendix 2, Table 35, for steam at 1 atm and 100°C
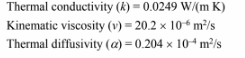
Parallel Wires: In the figure, a rectangular current loop is carrying current I1 = 7.0 A, in the direction indicated, near a long wire carrying a current Iw. The long wire is parallel to the sides of the rectangle. The rectangle loop has length 0.80 m and its sides are 0.10 m and 0.70 m from the wire. If the net force on the loop is to have magnitude 1.7 × 10-6 N and is to be directed towards the wire, what must be the magnitude and direction (from top to bottom or from bottom to top in the sketch) of the current Iw in the wire? (?0 = 4? × 10-7 T ? m/A)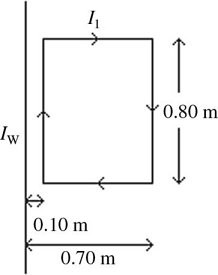
What will be an ideal response?
Glycerin at 30  has a density of 1,260
has a density of 1,260 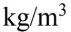 and a viscosity of 0.630 Pa-s. The glycerin is poured through a funnel with a neck that is 10.0 cm long and 1.00 cm in diameter. If the level of glycerin is kept at a level 5.00 cm above the neck, then what is the flow rate of the glycerin through the funnel?
and a viscosity of 0.630 Pa-s. The glycerin is poured through a funnel with a neck that is 10.0 cm long and 1.00 cm in diameter. If the level of glycerin is kept at a level 5.00 cm above the neck, then what is the flow rate of the glycerin through the funnel?
A. 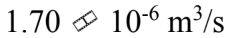
B. 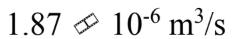
C. 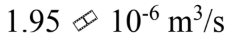
D. 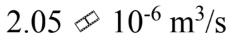
E. 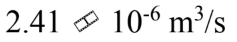
Which of these situations is possible?
1.Energy is transferred by heat to a system and the internal energy of the system decreases. 2.Energy is transferred by heat to a system and the internal energy of the system remains constant. 3.Energy is transferred by heat to a system and the internal energy of the system increases. 4.All of these are possible.