Everything else held constant, in the market for reserves, when the federal funds rate is 3%, lowering the interest rate paid on excess reserves rate from 2% to 1%
A) lowers the federal funds rate.
B) raises the federal funds rate.
C) has no effect on the federal funds rate.
D) has an indeterminate effect on the federal funds rate.
C
You might also like to view...
If a rise in the price of good X causes the quantity demanded of good X to fall, then
a. the Engel curve for good X is downward sloping. b. the (ordinary) demand curve for good X is downward sloping. c. the demand for good X is elastic. d. good X must be a Giffen good.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as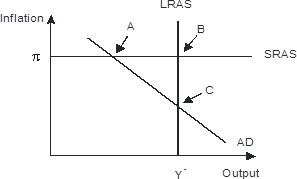
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Because a price floor causes:
A. a shortage, some form of rationing must occur. B. a surplus, some producers may ultimately lose because they won't have enough customers. C. a shortage, rent-seeking will occur. D. a surplus, everyone will be better off.
An increase in the real interest rate on U.S. bonds, everything else equal, will have the following impact on the foreign exchange market:
A. the supply of dollars will increase. B. the dollar will depreciate relative to foreign currencies. C. there will be a movement up the existing demand for dollars curve. D. the demand for dollars will increase.