You are assessing a patient who is complaining of chest pain that started about 45 minutes ago. His skin is pale and clammy and he has very little energy. His vital signs are respirations of 24, pulse of 120, and BP of 94/70. What priority would you give this patient?
A. High because of the blood pressure reading.
B. Low because his respiratoires are normal.
C. High because of the elevated pulse.
D. Low unless there is breathing difficulty.
Answer: A. High because of the blood pressure reading.
You might also like to view...
In the embryo, parallel ridges named digital rays are visible. Which structures will they become?
A. Fingers and toes B. Leg and forearm C. Ribs and vertebrae D. Tarsals and metatarsals E. The ulna and radius
Using the figure below, identify the labeled part.
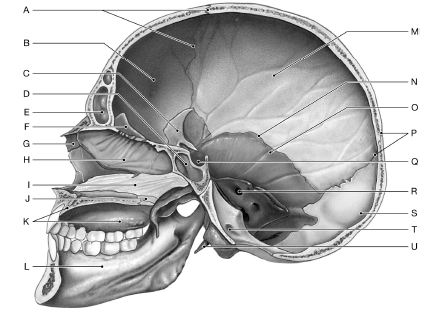
1) Label A: ______________________________
2) Label B: ______________________________
3) Label C: ______________________________
4) Label D: ______________________________
5) Label E: ______________________________
6) Label F: ______________________________
7) Label G: ______________________________
8) Label H: ______________________________
9) Label I: ______________________________
10) Label J: ______________________________
11) Label K: ______________________________
12) Label L: ______________________________
13) Label M: ______________________________
14) Label N: ______________________________
15) Label O: ______________________________
16) Label P: ______________________________
17) Label Q: ______________________________
18) Label R: ______________________________
19) Label S: ______________________________
20) Label T: ______________________________
21) Label U: ______________________________
Half of the fibers of each optic nerve decussate at the ________.
A. lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus B. midbrain C. optic chiasm D. superior colliculus E. optic foramen
Although most hernias are not painful, pain in the groin area can be one of the symptoms.
a. true b. false