If the price of imported inputs suddenly rises,
a) we buy less, so aggregate demand falls
b) we pay more for the same quantity, so aggregate demand rises
c) we substitute domestic sources of inputs, so aggregate demand rises
d) our ability to produce is reduced, so aggregate supply shifts inward
e) GDP in unaffected because imports are netted out of gross domestic product
d) our ability to produce is reduced, so aggregate supply shifts inward
You might also like to view...
All of the following are true EXCEPT
a. President Reagan was the first U.S. president to call for the use of economic criteria when evaluating policy b. President Reagan’s Executive Order 12291 required the use of a Regulatory Impact Analysis (RIA) when major regulations were being considered c. During his presidency, Clinton did not issue any executive order to continue Reagan’s commitment to using economic criteria in policy evaluation d. President Obama issued an executive order to support and expand upon President Clinton’s executive order requiring benefits to justify the costs of a significant regulation
Which of the following is NOT associated with the new Keynesian economics?
A) small-menu cost theory B) market-clearing models to explain business cycles C) inflation dynamics D) sticky-price theories of real GDP determination
______ occurs when voters look at the past performance of incumbent parties to decide how to vote in the current election.
A. Prospective voting B. Accountability C. Immobilism D. Retrospective voting
Refer to the given data. Suppose that the union that provides labor to firms in this market successfully negotiates an increase in the wage rate from $10 to $12. As a result of the wage increase, firms will hire:
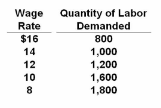
A. fewer workers and the total paid out for wages will decline.
B. fewer workers, but the total paid out for wages will increase.
C. fewer workers, but the total paid out for wages will remain unchanged.
D. more capital, if capital and labor are used in fixed proportions in production.