Everything else remaining unchanged, the effect of domestic spending shocks on a country with a floating exchange rate differs depending on
A. the mobility of capital across countries.
B. the interest rate differential between the country and its trading partners.
C. the change in the domestic price level in the short run.
D. the current trade balance situation of the country.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If firms in a duopoly can successfully collude
A) each firm can earn an economic profit. B) the industry, that is, both firms taken together, can earn the maximum economic profit. C) the firms achieve a cooperative equilibrium. D) All of the above answers are true.
Refer to Table 2.3. Assume that 2010 is the base year. The GDP deflator for 2010 is
A) 67.1. B) 84.5. C) 100.0. D) 118.3.
A form of government spending that is not made in exchange for a currently produced good or service is called
a. a transfer payment. b. consumption. c. investment. d. None of the above is correct.
In the graph below, the price of capital is $500 per unit. At point A, the firm can exchange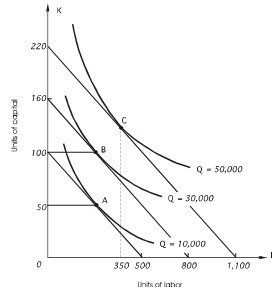
A. 5 units of capital for 1 unit of labor and keep cost unchanged. B. 5 units of capital for 1 unit of labor and keep output unchanged. C. 1 unit of capital for 5 units of labor and keep output unchanged. D. both b and c E. none of the above