Life-cycle saving is saving:
A. for protection against unexpected setbacks, such as the loss of a job or a medical emergency.
B. to pay life-insurance premiums.
C. for the purpose of leaving an inheritance.
D. to meet long-term objectives, such as retirement, college attendance, or the purchase of a home.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Refer to the accompanying figure. As the production of pizza increases, the opportunity cost of producing pizza: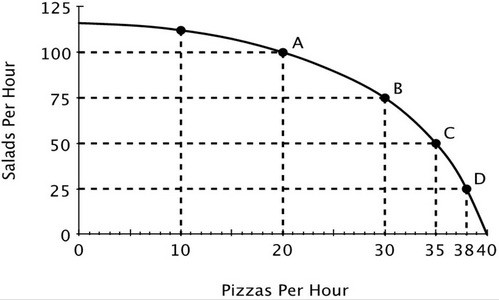
A. becomes negative. B. doesn't change. C. decreases. D. increases.
A price ceiling that is set above the equilibrium price will result in:
A. a loss in total economic surplus. B. a market price that is above the equilibrium price. C. no change in total economic surplus. D. an increase in consumer surplus.
Figure 4-21
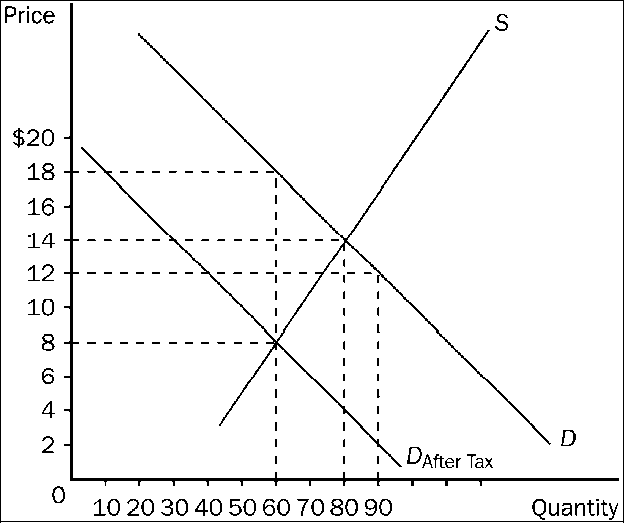
Refer to . How much tax revenue does this tax produce for the government?
a.
$480
b.
$600
c.
$800
d.
$1,080
Which curve(s) does the marginal cost curve intersect at the (their) minimum point?
A. Average total cost curve and average variable cost curve B. Average variable cost curve C. Average total cost curve D. Average fixed cost curve