For a firm selling its product in a purely competitive market, the marginal revenue product of labor can be found by:
A. adding marginal product to total product as one more unit of labor is employed.
B. adding marginal revenue to total product as one more unit of labor is employed.
C. multiplying marginal product by product price.
D. dividing marginal product by product price.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
An economic agent ________ when he accounts for the full costs and benefits of his actions
A) is called a free rider B) internalizes an externality C) maximizes his profit D) is called a rent seeker
Suppose chocolate-dipped strawberries are currently selling for $30 per dozen, but the equilibrium price of chocolate-dipped strawberries is $20 per dozen. We would expect a
a. shortage to exist and the market price of chocolate-dipped strawberries to increase. b. shortage to exist and the market price of chocolate-dipped strawberries to decrease. c. surplus to exist and the market price of chocolate-dipped strawberries to increase. d. surplus to exist and the market price of chocolate-dipped strawberries to decrease.
Maximizing total benefits is equivalent to maximizing net benefits if and only if there are:
A. increasing costs associated with achieving more benefits. B. constant marginal costs associated with achieving more benefits. C. no costs associated with achieving more benefits. D. decreasing costs associated with achieving more benefits.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.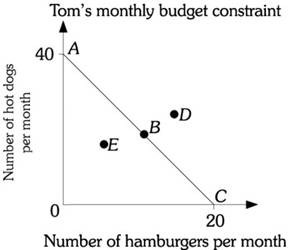 Figure 6.1Refer to Figure 6.1. Assume Tom's budget constraint is AC. If the price of a hot dog is $3, the price of a hamburger is
Figure 6.1Refer to Figure 6.1. Assume Tom's budget constraint is AC. If the price of a hot dog is $3, the price of a hamburger is
A. $1.50. B. $3. C. $6. D. $12.