Firm X belongs to Country A and Firm Y belongs to Country B. The two firms are a global duopoly. Each is considering initiating exports to a large foreign country that currently has no imports and no domestic production or consumption of this product. The figure shows the payoffs if neither, one, or both of the firms initiates exports of this product. Explain why this game has no clear solution, so both firms could decide not to export. Explain why country B's government should consider subsidizing Firm Y's exports.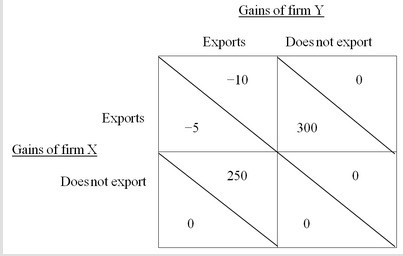
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE: The figure shows the payoffs for both firms when no subsidies are given. The rivalry game without subsidies has no clear-cut result. If one of the firms decides to export, it is best for the other firm not to export. Each firm would like to be the only exporter, but if both export both will lose. If the firms are unable to coordinate, both firms could decide not to export.
Should Country B's government offer a subsidy to Firm Y's exports? The subsidy could induce Firm Y to export regardless of what Firm X does. The subsidy would have to be at least $11. Let's say the subsidy is actually $15. Then the payoffs for both firms with the subsidy to exports by Firm Y are now: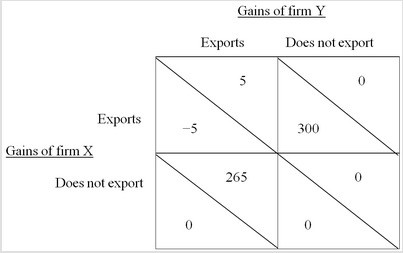
With the export subsidy, Firm Y should export regardless of what Firm X does. Knowing that Firm Y will export, Firm X will find it best not to export, and Firm Y will serve the entire foreign market. Firm Y, Country B, and the world as a whole would gain, compared to no production by either firm.
You might also like to view...
Higher interest rates increase both consumption and investment spending
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Intertemporal decisions involve economic decisions
A) made within a given period of time. B) made in between two periods of time. C) involving trade-offs across periods of time. D) that ignore concerns about the future.
Economic costs of an input include
A) only implicit costs. B) only explicit costs. C) both implicit and explicit costs. D) whatever management wishes to report to the shareholders.
The consumption function expresses the:
a. relation between consumption and dissaving. b. relation between consumption and disposable personal income. c. purposes of consumption. d. relation between consumption and dissaving.