Biometric performance factors that need to be considered include accuracy, speed, reliability, acceptability, cost, resistance to counterfeiting, enrollment time, database storage requirements, and intrusiveness.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
True
You might also like to view...
What are the functions of IMAP?
What will be an ideal response?
(Simulation: The Tortoise and the Hare) In this exercise, you’ll re-create the classic race of the tortoise and the hare. You’ll use random number generation to develop a simulation of this memorable event.
Our contenders begin the race at “square 1” of 70 squares. Each square represents a possible position along the race course. The finish line is at square 70. The first contender to reach or pass square 70 is rewarded with a pail of fresh carrots and lettuce. The course weaves its way up the side of a slippery mountain, so occasionally the contenders lose ground. There is a clock that ticks once per second. With each tick of the clock, your program should use function moveTortoise and moveHare to adjust the position of the animals according to the rules in Fig. 7.21. These functions should use pointer-based pass-by-reference to modify the position of the tortoise and the hare.
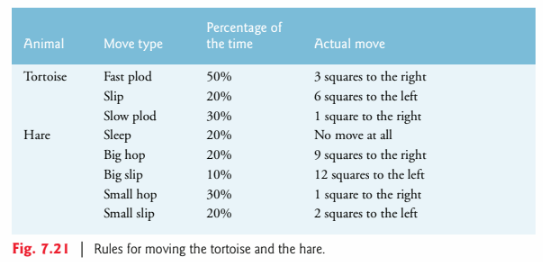
Use variables to keep track of the positions of the animals (i.e., position numbers are 1–70). Start each animal at position 1 (i.e., the “starting gate”). If an animal slips left before square 1, move the animal back to square 1. Generate the percentages in the preceding table by producing a random integer i in the range
1 ? i ? 10. For the tortoise, perform a “fast plod” when 1 ? i ? 5, a “slip” when 6 ? i ? 7 or a “slow plod” when 8 ? i ? 10. Use a similar technique to move the hare. Begin the race by printing
BANG !!!!!
AND THEY'RE OFF !!!!!
For each tick of the clock (i.e., each repetition of a loop), print a 70-position line showing the letter T in the tortoise’s position and the letter H in the hare’s position. Occasionally, the contenders land on the same square. In this case, the tortoise bites the hare and your program should print OUCH!!! beginning at that position. All print positions other than the T, the H or the OUCH!!! (in
case of a tie) should be blank. After printing each line, test if either animal has reached or passed square 70. If so, print the winner and terminate the simulation. If the tortoise wins, print TORTOISE WINS!!! YAY!!! If the are wins, print Hare wins. Yuch. If both animals win on the same clock tick, you may want to favor the tortoise (the “underdog”), or you may want to print It's a tie. If neither animal wins, perform the loop again to simulate the next tick of the clock.
If a user is having a problem logging in to a company intranet, what test can you make from another computer on the network to determine if the user's computer is up, the TCP/IP protocol is working, and the system is connected to the network?
What will be an ideal response?
The Compatibility Checker summarizes the issues that it finds within the dialog box and can create a worksheet that contains a list of issues.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)