Suppose there is a semiskilled labor market and two different unskilled labor markets. Initially, all three markets are in competitive equilibrium. What would happen if the government imposed a minimum wage rate above the competitive equilibrium rate in one of the unskilled labor markets?
a. Wage rates will rise in all three markets.
b. Wage rates will rise in both unskilled labor markets, but remain unchanged in the semiskilled labor sector.
c. Wage rates will rise in the semiskilled labor market and in the unskilled labor market covered by the minimum wage, but fall in the other unskilled labor market.
d. Wage rates will rise in the unskilled labor market covered by the minimum wage, remain unchanged in the other unskilled labor market, and fall in the semiskilled labor market.
e. Wage rates will rise in the unskilled labor market covered by the minimum wage, but remain unchanged in the other two markets.
C
You might also like to view...
Use the following consumption schedule to answer the next question. 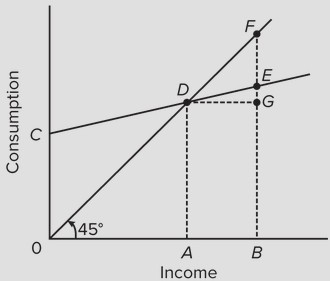 The marginal propensity to consume is represented by
The marginal propensity to consume is represented by
A. GE/AB. B. EF/BE. C. GF/BE. D. DE/AB.
The three functions of money are
A. implementing monetary policy, fiscal policy, and structural policy. B. spending for consumption, investment, and government purchases. C. serving as a medium of exchange, unit of account, and store of value. D. measuring balance of payments, exchange rates, and interest rates.
An increase in technology will always produce economic growth in society
A. True B. False
A firm in perfect competition and one in monopolistic competition are very similar in that MR = P for firms in both markets.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)