Which of the following describes that people cannot examine every possible choice available to them but instead use simple rules of thumb to sort among the alternatives that happen to occur to them?
A) self-interest
B) bounded rationality
C) ceteris paribus
D) normative economics
B
You might also like to view...
In the situation involving a bilateral monopoly, a
A) single firm acts as both the monopsonist and the monopoly. B) single seller sells to a single buyer. C) monopsonist sells to a monopsonist. D) monopolist sells to a monopolist.
Wally owns a dog whose barking annoys Wally's neighbor, Corrine. Suppose that the benefit of owning the dog is worth $700 to Wally and that Corrine bears a cost of $500 from the barking. Assuming Wally has the legal right to keep the dog, a possible private solution to this problem is that
a. Wally pays Corrine $600 for her inconvenience. b. Corrine pays Wally $400 to give the dog to his parents who live on an isolated farm. c. Corrine pays Wally $550 to give the dog to his parents who live on an isolated farm. d. The current situation is efficient.
Which of the following is the best example of a perfectly competitive market?
A.) The automobile industry. B.) The soft drink industry. C.) Dairy farming. D.) Fast-food restaurants
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 the result in the long run would be: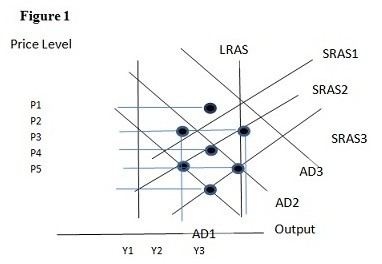
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y2. C. P3 and Y1. D. P2 and Y3.