Discuss some of the government regulations designed to ensure depositors' safety and to control the money supply
Deposit insurance: The principal innovation that guarantees the safety of bank deposits is deposit insurance. Most U.S. bank deposits are insured against loss by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)?an agency of the federal government.
Bank supervision: Various regulatory authorities conduct periodic bank examinations to keep tabs on the financial conditions and business practices of the banks under their purview. After a rash of bank failures in the late 1980s and early 1990s, U.S. bank supervision was tightened by legislation that permits the authorities to intervene early in the affairs of financially troubled banks. The 2007-2009 financial crisis led to the passage of the Dodd-Frank Act which empowered the Federal Reserve to supervise financial institutions deemed to be systemically important and subject these institutions to a more stringent regulatory regime than other banks.
Reserve requirements: A final type of regulation also has some bearing on safety but is motivated primarily by the government's desire to control the money supply. The amount of money any bank will issue depends on the amount of reserves it elects to keep. For this reason, most banks are subject by law to minimum required reserves.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 20-13. Consider a simple economy that produces only three products: tacos, earplugs, and toothbrushes. Use the information in the table to calculate the inflation rate for 2016, as measured by the consumer price index
What will be an ideal response?
Diversified companies show above average performance because risk is better managed
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
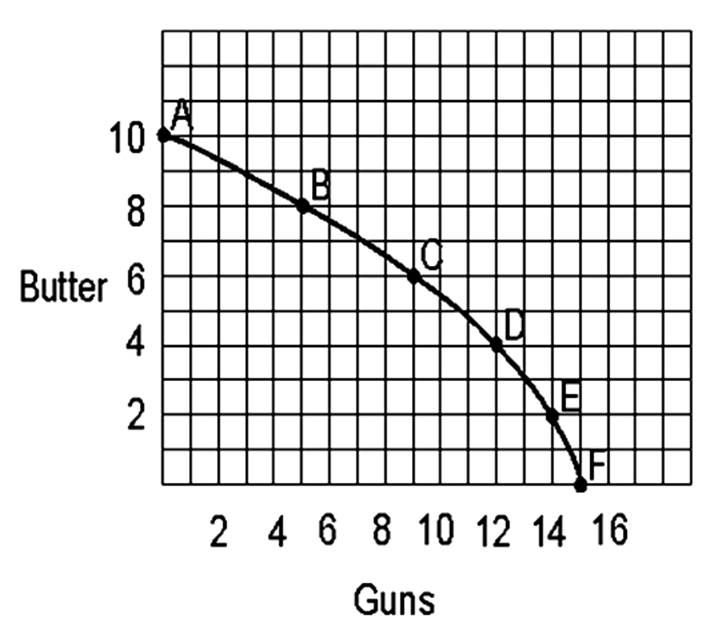
A country producing a combination of 9 units of guns and 6 units of butter would be _____________ (outside/on/inside) the production possibilities curve.
One implication of the median voter model is that a candidate is likely to label himself __________ and his or her opponent as __________
A) moderate; too far right or too far left (whichever makes more sense) B) a member of one of the political wings; moderate or mainstream C) as a member of the political right; moderate D) as a member of the political left; moderate E) none of the above