Where do the ocean's salts originate?
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: One source is the chemical weathering of continental rocks. As rocks weather, elements such as sodium, calcium, and potassium dissolve into the water that flows downstream to eventually make its way to the ocean. Earth's interior is another source. Throughout Earth's history, volcanic eruptions have delivered huge quantities of chlorine, as well as water vapor and other gases, to the ocean. Chlorine plus sodium? Sodium chloride—common table salt. Hence, the ocean's salty taste.
You might also like to view...
Might a region of intergalactic [between the galaxies] space, containing no material particles, contain energy?
A) No, because only material particles can possess energy. B) No, because physically nothing exists except particles and empty space. C) No, for both of the above reasons. D) Yes, it might contain the thermal energy of intergalactic gases. E) Yes, in the form of electromagnetic fields and other force fields.
Light from a monochromatic source shines through a double slit onto a screen 5.0 m away. The slits are 0.18 mm apart. The dark bands on the screen are measured to be 1.7 cm apart. What is the wavelength of the incident light?
A) 457 nm B) 306 nm C) 392 nm D) 612 nm E) 784 nm
Dimensional Analysis: The gravitational force of attraction F between two tiny masses m1 and m2 that are separated by a distance r is F = G 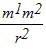 . In the SI system, force has units of kg ? m/s2 . Use the given gravitational force formula to determine the SI units of G in terms of the fundamental quantities of mass, length, and time.
. In the SI system, force has units of kg ? m/s2 . Use the given gravitational force formula to determine the SI units of G in terms of the fundamental quantities of mass, length, and time.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Which has the greater density?
A) a cup-full of fresh water B) a lake-full of fresh water C) both the same D) need more information