In an indifference curve diagram, the quantities of good Y are measured along the vertical axis and the quantities of good X are measured along the horizontal axis. The marginal rate of substitution is defined as
A) how much good Y you must give up to get one more unit of good X.
B) how much good Y you are willing to give up to get one more unit of good X.
C) the relative price of good Y in terms of good X.
D) how much you prefer to substitute good X for good Y.
B
You might also like to view...
Consider the production possibilities frontier displayed in the figure shown. A society should choose to produce:
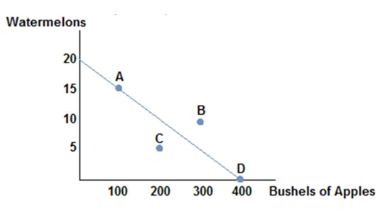
A. at point C because it is the safest.
B. at point B because it represents the most the society can produce.
C. at any point that produce some of each good.
D. at any point on the frontier rather than inside it.
Discuss how economists calculate NI, PI and DI
In the case of public goods, _____
a. the free rider problem does not arise b. one person's consumption of the good reduces the consumption of the good by others c. individuals can be easily excluded from consuming the good once it is provided d. the quantity produced by a private market would be too large from society's viewpoint e. the principle of mutual excludability and principle of rivalry do not apply
If Happy Cleaners and Sparkle Cleaners are in a Cournot oligopoly and Happy Cleaners has a higher cost of production than Sparkle? Cleaners, in? equilibrium, Happy Cleaners will produce? ________ than Sparkle Cleaners and earn an economic profit that is? ________ Sparkle Cleaners.
A) more; less than
B) less; less than
C) less; the same as
D) more; the same as