Suppose you have a firm in which the owner pays $10,000 per month on rent of the plant and equipment and will pay that regardless of much output they produce. If they get going they need $10 in materials and $20 in labor for each unit they produce,
A. their fixed costs are $10,000 and $10 per unit.
B. their fixed costs are $10,000 and variable costs are $30 per unit.
C. their fixed costs are $10,000 and variable costs are $20 per unit.
D. their variable costs are $10,000 plus $10 per unit.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
When a simple monopolist chooses to sell an additional unit of a good or service
a. marginal revenue will be equal to the going market price. b. marginal revenue will always be negative. c. it will only have to lower its price on the additional unit. d. it will have to lower its price on the additional unit and on all other units.
In the figure below, the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium at point A. If there is an adverse supply shock that reduces potential output and shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve from LRAS to LRAS', then there is initially ________ gap and the short-run aggregate supply curve will ________. 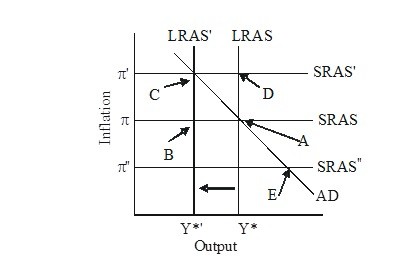
A. an expansionary: eventually shift to SRAS" B. a recessionary; eventually shift to SRAS' C. an expansionary; eventually shift to SRAS' D. a recessionary; eventually shift to SRAS"
Taxes levied on a firm's earnings ________ the effective cost of funds
A) lower B) raise C) have no effect D) none of the above
Which of the following statements is true of a barter system? a. In a barter system economy, no rates of exchange are defined
b. In a barter system economy, there are as many different rates of exchange as there are pairs of goods to trade. c. In a barter system economy, rates of exchange are expressed in goods per dollar. d. In a barter system economy, rates of exchange are expressed in dollars per good. e. In a barter system economy, rates of exchange are denominated in gold or silver.