The _________ provide passageways for spinal nerves to exit the vertebral column and travel to other parts of the body
A. vertebral foramina
B. intervertebral foramina
C. vertebral canals
D. articular facets
E. transverse foramina
B
You might also like to view...
The myelin sheath that covers many CNS axons is formed by
A) astrocytes. B) satellite cells. C) oligodendrocytes. D) microglia. E) ependymal cells.
Structure C is the
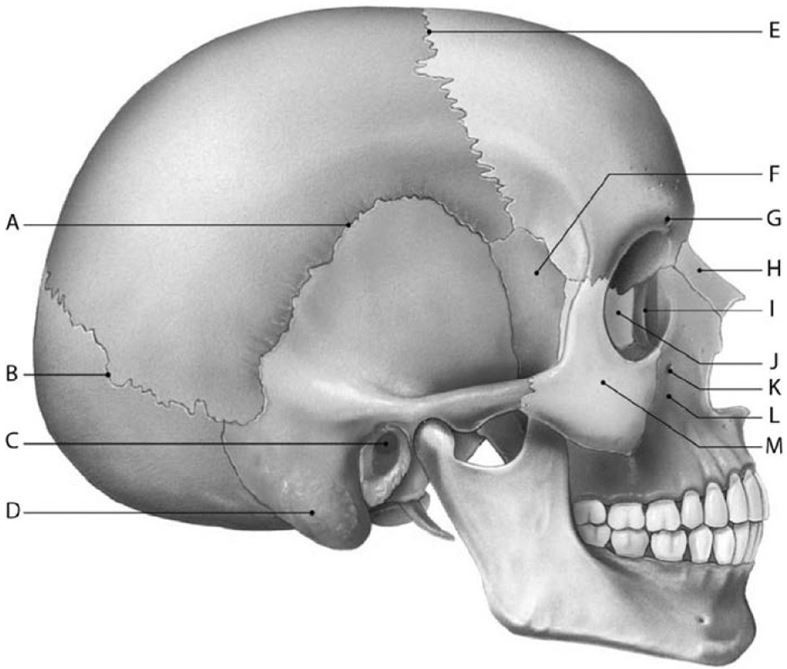
A) sella turcica.
B) styloid process.
C) mastoid process.
D) external auditory meatus.
E) coronoid process.
The parasympathetic division arises from the __________ regions of the spinal cord.
A. brain, thoracic, and lumbar B. brain, sacral, and coccygeal C. brain, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal D. sacral and lumbar E. brain and sacral
A 56-year-old man was admitted to the hospital with a myocardial infarction. At admission, his serum creatinine was 1.2 mg/dL, and his creatinine clearance was 100 mL/min
Over the next 3 days, he had several periods of hypotension, and his serum creatinine is now increased to 3.6 mg/dL. Assuming that he is in steady-state balance for creatinine (i.e., amount excreted = amounted produced), what is his predicted creatinine clearance? A. 10 mL/min B. 33 mL/min C. 50 mL/min D. 66 mL/min E. 100 mL/min