Marginal cost pricing means that a firm
A. Produces up to the output level at which MC = 0 for a given market price.
B. Lowers market price to marginal cost for a given output.
C. Produces up to the output where P = MC for a given market price.
D. Lets marginal cost rise to the market price for a given output.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
According to Keynesian economic theory, the government should spend money to pay down the national debt.
a. during an economic depression. b. in order to balance the budget. c. only if it is willing to raise taxes. d. on the military instead of on domestic issues.
A floating exchange rate
a. is determined by the national governments involved b. remains extremely stable over long periods of time c. is determined by the actions of central banks d. is allowed to vary only within a narrow range e. adjusts in response to market forces
Suppose there are three power-generating plants, each of which has access to 5 different production processes. The table below summarizes the cost of each production process and the corresponding number of tons of smoke emitted each. Process(smoke/day) A(4 tons/day) B(3 tons/day) C(2 tons/day) D(1 ton/day) E(0 tons/day) Cost to Firm X ($/day) $500$514$530$555$585 Cost to Firm Y ($/day) $400$420$445$480 $520Cost to Firm z ($/day) $300$325$360$400 $550If pollution is unregulated, then total daily smoke emission will be ________ tons.
A. 12 B. 4 C. 8 D. 9
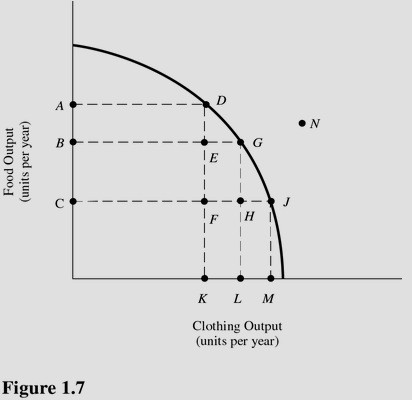 Refer to Figure 1.7. The cost of producing at point D rather than point J is
Refer to Figure 1.7. The cost of producing at point D rather than point J is
A. KM units of clothing. B. AC units of food. C. OA units of food. D. OM units of clothing.