An increase in short-run aggregate supply is
A) the result of an increase in the price level.
B) represented by a movement up along the SRAS curve.
C) represented by a rightward shift in the SRAS curve.
D) both a and b
E) both a and C
C
You might also like to view...
Player 1 and Player 2 are playing a game in which Player 1 has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Player 1 has chosen either Up or Down, Player 2, who can see what Player 1 has chosen, must choose Up or Down at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch. 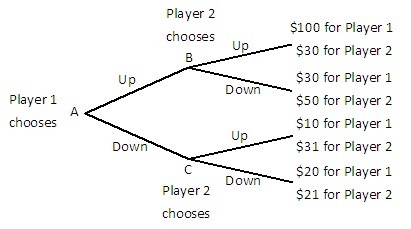 What is the equilibrium outcome of this game?
What is the equilibrium outcome of this game?
A. Player 1 chooses Up and Player 2 chooses Down. B. Player 1 chooses Down and Player 2 chooses Up. C. Player 1 and Player 2 both choose Down. D. Player 1 and Player 2 both choose Up.
The long-run aggregate supply line is:
A. downward sloping. B. upward sloping. C. vertical at the economy's actual output. D. vertical at the economy's potential output.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 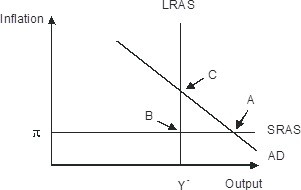
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Explain what happens to the magnitude of price elasticity of demand as price increases along a straight-line demand curve.
What will be an ideal response?