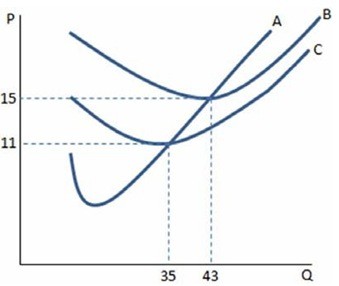
 If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown and produces at the profit-maximizing level of output, which of the following is true? A firm will:
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown and produces at the profit-maximizing level of output, which of the following is true? A firm will:
A. plan to exit the industry in the long run if price falls below $15.
B. continue to operate in the short run if price is below $11.
C. will earn maximum profits at a quantity of 35.
D. make positive profits any time the price is greater than $11.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Trade restrictions can prevent purchasing power parity from holding because:
A. the time and energy of importation paperwork can add to the cost of the good sold. B. tariffs can add to the cost of the good sold. C. they can add costs to the selling price because they add to the seller's cost. D. All of these statements are true.
The aggregate supply curve slopes
a. downward because firms can sell more at lower prices. b. downward because firms can hire more workers at lower prices. c. upward because firms want to hire more workers at higher wage levels. d. upward because firms can hire labor at fixed wages for short-run periods.
The consumption component of GDP includes spending on
a. durable goods and nondurable goods, but not spending on services. b. durable goods and services, but not spending on nondurable goods. c. nondurable goods and services, but not spending on durable goods. d. durable goods, nondurable goods, and services.
Figure 2-9
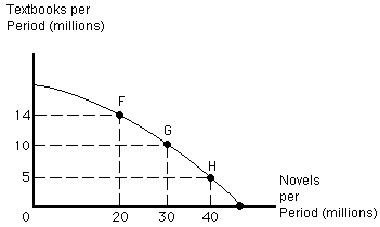
Assume that the publishing industry produces novels and textbooks, as shown in the production possibilities frontier in . Moving from point H to G, the opportunity cost of those five additional textbooks equals
a.
0.5 novels
b.
10 million novels
c.
3 novels
d.
8 novels
e.
2 novels