(a) Find the total profit or total loss of the firm shown in the graph below. (b) Is the firm in short run or long run? (c) How much is the firm's most efficient output? (d) What is the lowest price the firm would accept in the long run?
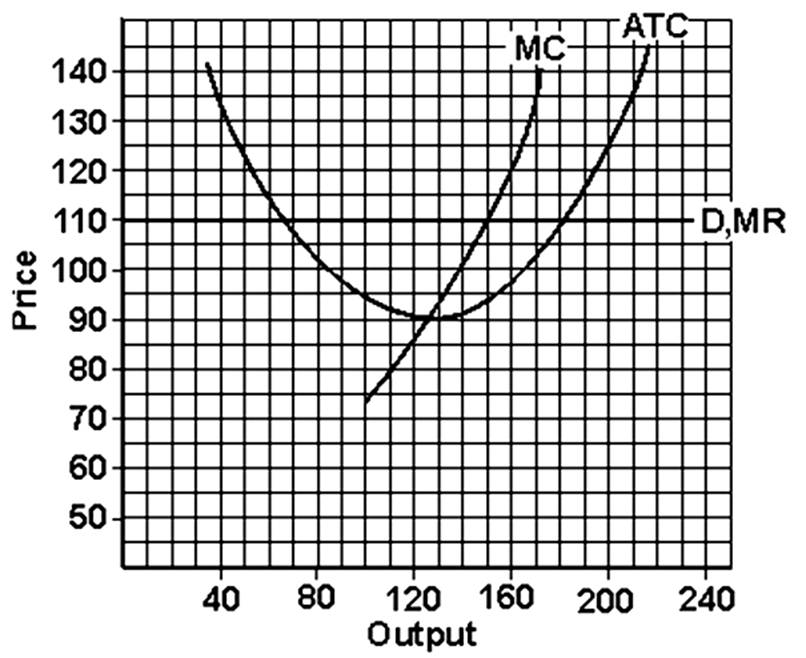
(a) Total profit = (price - ATC) × output
= ($110 - 94) 150
= $16 × 150
= $2,400
(b) short run; (c) 125; (d) $90
You might also like to view...
The owner of a pizza shop observes that when she raises the price of a large pizza, her total revenue decreases, and when she lowers the price of a large pizza, her total revenue increases. This suggests that:
A. pizza lovers act irrationally. B. the demand for her large pizzas is inelastic with respect to price. C. the demand for her large pizzas is elastic with respect to price. D. there are few good substitutes for a large pizza.
Which of the following was NOT one of the causes of the Asian financial crises of 1997 and 1998?
A) A current account deficit and financial account surpluses B) The use of exports as an engine of economic growth by the countries involved C) China's 1994 devaluation of its fixed exchange rate D) The appreciation of the U.S. dollar and depreciation of the Japanese yen E) Crony capitalism
Consider the model: yt= 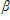
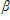
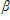
the condition sufficient for consistency of OLS is:
A. E(zt1|zt2) = 0.
B. E(yt |zt1, zt2) = 0.
C. E(ut |zt1, zt2) = 0.
D. E(ut |zt1, zt2) = .
Why do corporate boards of directors sometimes link top managers' compensation to the corporations' stock prices? How might tying compensation too closely to stock prices create an incentive for corporate fraud
What will be an ideal response?