Refer to Figure 28-9. A follower of the new classical macroeconomics would argue that a contractionary monetary policy to lower inflation after a supply shock, like that pursued by Volcker in 1979, would result in a movement from
A) C to D to A. B) A to B. C) C to A. D) A to C. E) A to D to C.
C
You might also like to view...
A demand curve can be interpreted as
A) a marginal benefit curve. B) a total benefit curve. C) an average benefit curve. D) a marginal cost curve. E) None of the above answers is correct.
Which of the following would economic freedom lead to?
a. A higher standard of living b. Better living conditions c. Longer life expectancy d. Better education e. All of these
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good, as well as a tariff and the world price for that good.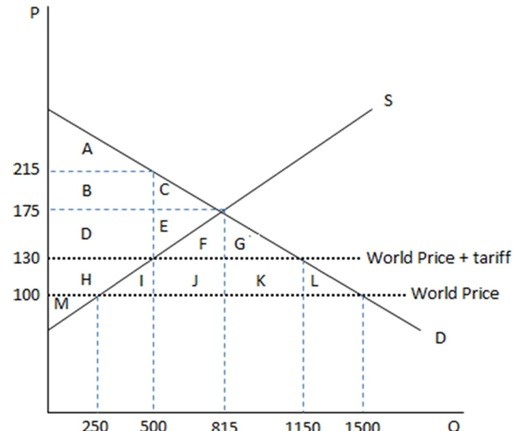 According to the graph shown, if the economy were operating under free trade and then imposed a tariff, the overall impact on surplus would be a net:
According to the graph shown, if the economy were operating under free trade and then imposed a tariff, the overall impact on surplus would be a net:
A. gain of IJKL. B. loss of IJKL. C. gain of FGHIJKL. D. loss of IL.
If the price of a good rises by 10% and the percentage decrease in the total amount consumers spend on the good is 10%, then the good is
A. unit elastic. B. inelastic. C. elastic. D. perfectly inelastic.