Compare Pareto optimality with the utilitarian view that says we are better off when the overall gain in utility exceeds the overall loss in utility by the consumers. What are the effects of the differences for policy? Can this concept be applied to public goods?
What will be an ideal response?
Pareto optimality requires that no one be hurt at all in any exchange. Either both or at least one party will have to be enhanced while no negative impact occurs. This leaves out many exchanges where one party would gain a lot while the other party would lose only a small amount. Any one person has the right to veto a proposed change, and so the status quo is much more likely to prevail. This veto right is fundamental to freedom in the marketplace. No one should be coerced into an exchange that makes them worse off. This concept works in the area of purely private goods, but is difficult to apply where public goods are involved. With public goods, individuals can consume without paying if they hide their preferences, so Pareto optimality is difficult to employ. However imperfectly, collective decisions, like the allocation of resources to public goods, require a weighing of collective benefits and costs through an appropriate public policy process.
You might also like to view...
Given a demand function of Qd = D(P) = 500 - 10P, what is the inverse demand function?
A. D(P) = 50 - P B. P(Q) = 50P C. P(Q) = 50 - (Q/10) D. P(Q) = 500 - 10Q
An increase in which of the following variables will cause an increase in the user cost of capital?
A) rt B) ?t C) ?et D) all of the above E) none of the above
If the government increases taxes, the
A. aggregate supply decreases. B. aggregate demand decreases. C. aggregate supply increases. D. aggregate demand increases.
The following is an investment schedule. Investment spending is in billions of dollars.
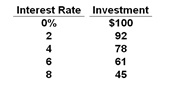
Refer to the data in the table above. When the government runs a budget deficit and issues more Treasury securities, crowding out would occur if:
A. The interest rate is at 0%
B. The interest rate rises
C. The interest rate falls
D. The interest rate stays high at 8%