The "Big Mac Theory of Exchange Rates" tests the accuracy of the purchasing power parity theory. In July 2015, the Economist reported that the average price of a Big Mac in the U.S. was $4.79
In Sweden, the average price of a Big Mac at that time was 43.7 kronor. What is the "implied exchange rate" between Swedish kronor and U.S. dollars?
A) 0.11 kronor per dollar B) 1.90 kronor per dollar
C) 9.12 kronor per dollar D) 46.2 kronor per dollar
C
You might also like to view...
Differences in marginal revenue products are the most important factor in explaining wage differences. Other factors that explain wage differences include all but one of the following. Which factor does not help explain differences in wages?
A) discrimination B) labor unions C) compensating differentials D) cognitive differentials
General equilibrium analysis
A. concerns competitive equilibrium only in the factor markets. B. concerns competitive equilibrium only in the product markets. C. concerns competitive equilibrium in a single market, considered in isolation. D. is the study of competitive equilibrium in many markets at the same time.
Refer to the table below. The perfectly competitive market for dairy products has a 40 percent chance of a high price of $3.00 and a 60 percent chance of a low price of $2.00. To maximize expected profit, Happy Cows should produce ________ units and Free Cows should produce ________ units.
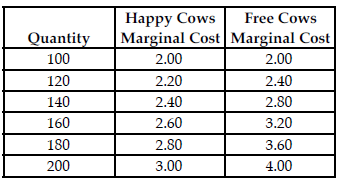
Happy Cows and Free Cows are two separate perfectly competitive dairy farms. The table above shows the respective firms' marginal cost at various production levels.
A) 120; 120
B) 140; 120
C) 120; 140
D) 140; 140
Jim enjoys the feeling of wind in his hair enough to ride his motorcycle without a helmet, even though he fully realizes the potential for injury it creates by not wearing one in the unlikely event he is in an accident. To an economist, Jim is
a. making an irrational choice. b. making a rational choice. c. not fully considering the personal costs and benefits of his decision. d. not responding to the incentives he faces.