Briefly describe the star-gas-star cycle
What will be an ideal response?
During a star's lifetime, it fuses hydrogen into helium and helium into carbon. If it is more massive, it also creates heavier elements, up to iron, by fusion, and even heavier elements, up to uranium, during a supernova event. When the star ends its life as a planetary nebula or in a supernova explosion, it disperses these elements into the interstellar medium. The interstellar medium thus gains these heavier elements and has a smaller proportion of hydrogen but a larger proportion of heavier elements than it did before. The interstellar medium cools, forms molecular clouds, and then forms new stars, which are made out of the material of the interstellar medium.
You might also like to view...
Simple Pendulum: As shown in the figure, a 0.23-kg ball is suspended from a string 6.87 m long and is pulled slightly to the left. As the ball swings through the lowest part of its motion it encounters a spring attached to the wall. The spring pushes against the ball and eventually the ball is returned to its original starting position. Find the time for one complete cycle of this motion if the spring constant (force constant) is 19 N/m. (Assume that once the pendulum ball hits the spring there is no effect due to the vertical movement of the ball.)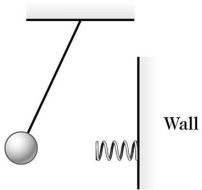
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
The radiation our eyes are most sensitive to is the color
A) black at 227 nm. B) blue at 4,321 nm. C) violet at 7,000 Angstroms. D) yellow-green at about 550 nm. E) red at 6563 Angstroms.
If the length of a wire increases, its resistance decreases
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
A constant current I in a coil of inductance L does not produce an emf in that coil
Indicate whether the statement is true or false