Asteroids Object Model Develop an analysis object model based on the use cases elicited for the Asteroids problem statement: Examine all Asteroids use cases and identify the most important objects. Differentiate between entity, control and boundary objects. Use generalization to avoid redundancies.
Asteroids Dynamic Model
a) Object Interaction
Use sequence diagrams to show how the objects you found work together.
Concentrate on how solid bodies are moved and their position is calculated.
b) Flow
Use activity diagrams to show how a collision between solid bodies (e.g.
asteroids, space shuttles and rockets) is recognized and handled.
Categorizing Objects
Consider a file system with a graphical user interface, such as Macintosh’s Finder,
Microsoft’s Windows Explorer, or KDE’s Konqueror. The following objects were
identified from a use case describing how to copy a file from a CD to a hard disk:
File, Icon, TrashCan, Folder, Disk and Pointer. Specify which are entity
objects, which are boundary objects, and which are control objects.
Sequence Diagrams
Assuming the same file system as before, consider a scenario consisting of
selecting a file on a CD, dragging it to a folder and releasing the mouse. Arrange the
objects listed in Homework 1 and a dedicated control object for this scenario,
DragAndDropControl, horizontally on a sequence diagram. Place the boundary
objects on the left, then the control object DragAndDropControl, and finally, the
entity objects. Draw the sequence of interactions resulting from dropping the file into
a folder. For now, ignore the exceptional cases.
State Diagrams
Consider a traffic light system at a four-way crossroads (e.g., two roads intersecting
at right angles). Assume the simplest algorithm for cycling through the lights (e.g., all traffic on one road is allowed to go through the crossroad while the other traffic is
stopped). Identify the states of this system and draw a statechart describing them.
Remember that each individual traffic light has three states (i.e. green, yellow, and
red). Your statechart must not allow potentially dangerous light combinations (e.g.
all green or green/yellow on crossing streets).
1) Draw a use case diagram showing all use cases you can identify. It should
contain actors and relationships as well.
2) Provide a textual description of 3 of the identified use cases. Use the template
from the OOSE Book1.
3) Do a syntactical analysis of the flows of events using Abbott’s technique.
Deliverable is a class diagram of the identified classes.
4) Use the identified classes to draw a sequence diagram per use case and follow
the heuristics for sequence diagrams.
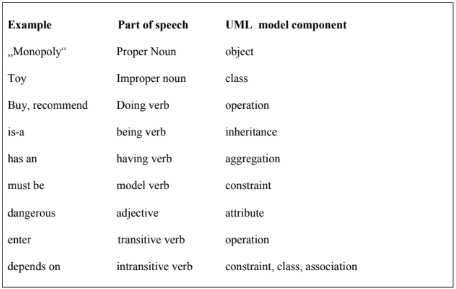
Abbot Analysis
Our application domain is the airport. Consider the following scenario:

You might also like to view...
Which of the following would be the best function prototype for a function that subtracts the corresponding elements of two arrays:
a) void subtractArray (int a[ ], int b[ ], int c[ ]) b) void subtractArray (const int a[ ],const int b[ ], int c[ ]) c) void subtractArray (const int a[ ],const int b[ ], int c[ ], const int) d) void subtractArray (const int a[ ], const int b[ ],const int c[ ], const int)
Which of the following is a computer-related mistake?
A. Operating unintegrated information systems. B. Mishandling computer outputs. C. Acquiring redundant systems. D. Exhausting information system resources.
A(n) ____ often can help convey relationships between key points in your presentation.
A. illustration B. slide background color C. text box D. worksheet
Even though you should handle the visual display of content with CSS, you can use several types of built-in formatting options without CSS.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)