The mass of Jupiter can be calculated by
A) measuring the orbital period and distance of Jupiter's orbit around the Sun.
B) measuring the orbital period and distance of one of Jupiter's moons.
C) measuring the orbital speed of one of Jupiter's moons.
D) knowing the Sun's mass and measuring how Jupiter's speed changes during its elliptical orbit around the Sun.
E) knowing the Sun's mass and measuring the average distance of Jupiter from the Sun.
B
You might also like to view...
What is a meteoroid?
A. a space rock that survives its fall through Earth's atmosphere and reaches the ground B. any one of the large rocky bodies that orbit the Sun, primarily between Jupiter and Saturn C. a glowing trail of hot gas and debris heated by friction as an object moves through the atmosphere D. the object that causes a "shooting star," but before it passes through the atmosphere
A particle (charge = Q) is kept in a fixed position at point P, and a second particle (charge = q) is released from rest when it is a distance R from P. If Q = +2.0 mC, q = ?1.5 mC, and R = 30 cm, what is the kinetic energy of the moving particle after it has moved a distance of 10 cm?
a. 60 kJ b. 45 kJ c. 75 kJ d. 90 kJ e. 230 kJ
A solar or lunar eclipse will occur
a. when the Sun is near the line of nodes of the Moon, and the Moon is new or full. b. any time the Moon is new or full. c. when the Sun is near the solstice, and the Moon is new or full. d. half-way through an eclipse year. e. when the Sun is near the equinox, and the Moon is new or full.
Momentum: A tiger is running in a straight line. If we double both the mass and speed of the tiger, the magnitude of its momentum will increase by what factor?
A. 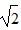
B. 2
C. 4
D. 8
E. 16