The amount by which consumption increases when after-tax income increases by $1 is called the:
A. marginal propensity to consume.
B. consumption multiplier effect.
C. marginal consumption revenue.
D. variable propensity to consume.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Monopoly market 1880 Town is a tourist attraction in Midland, SD. Owners of this attraction have collected buildings built between 1880 and 1920, filled them with antique furniture and collectables, and charge admission for tourists to experience history. Because of the exclusivity and location 1880 Town, this tourist attraction enjoys a measure of monopoly power. Suppose you run a tourist attraction similar to 1880 Town. After running some tests with pricing, you have formulated a daily demand schedule for admission as given. In addition to tracking demand at various price levels, you also monitor costs closely.
a) Using the demand schedule provided, find total revenue and marginal revenue at each point.
b) Using total costs, find marginal costs at each point. (Just as marginal revenue is the change in total revenue divided by a change in Q, marginal cost is the change in total cost divided by a change in Q.)
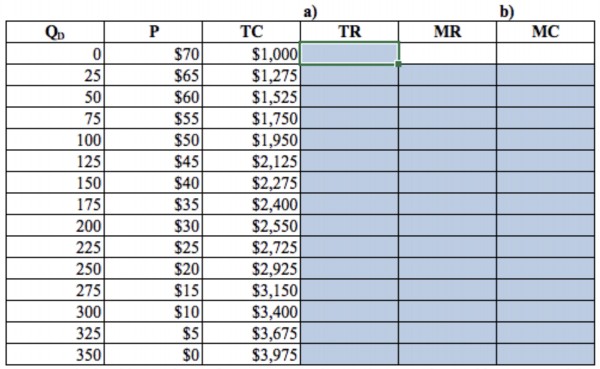
c) How much should you charge for entrance to the tourist attraction and how many visitors do you expect to have?
d) What is profit at this point?
A university raises annual tuition by 2 percent. No other events have occurred, and the university's revenues have increased. It must be TRUE that
A) the associated change in quantity demanded was smaller than 2 percent. B) the associated change in quantity demanded was equal to 2 percent. C) the associated change in quantity demanded was greater than 2 percent. D) there was no associated change in quantity demanded.
The notion of interest sensitive consumption would be most readily observed when people buy
A. food. B. cars. C. insurance. D. higher education.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. If the expected rates of return on investments increase, the loanable funds theory predicts that the equilibrium interest rate would decrease. 2. An increase in the expected rates of return on investments would most likely increase the supply of loanable funds. 3. Other things equal, short-term loans usually have lower rates of interest than do long-term loans. 4. For a given future value, the higher is the interest rate, the higher will be the present value. 5. In time-value of money calculations, discounting is the reverse of compounding.