In the Keynesian cross diagram, an increase in autonomous consumer expenditure causes the aggregate demand function to shift up, the equilibrium level of aggregate output to ________, and the IS curve to shift to the ________,
everything else held constant.
A) rise; left
B) rise; right
C) fall; left
D) fall; right
B
You might also like to view...
Suppose that the equilibrium nominal interest rate is 4 percent and the equilibrium quantity of money is $1 trillion. At any interest rate above 4 percent,
A) less than $1 trillion will be demanded and bond prices will fall. B) more than $1 trillion will be supplied and bond prices will fall. C) there is a shortage of money and the interest rate will rise. D) more than $1 trillion will be supplied and the interest rate will rise. E) less than $1 trillion will be demanded and bond prices will increase.
Refer to Figure 3-8. The graph in this figure illustrates an initial competitive equilibrium in the market for motorcycles at the intersection of D2 and S2 (point E)
If the technology to produce motorcycles improves and the number of buyers increases, how will the equilibrium point change? A) The equilibrium point will move from E to C. B) The equilibrium point will remain at E. C) The equilibrium point will move from E to B. D) The equilibrium point will move from E to A.
Using the information in the table shown, the marginal revenue:
This table represents the revenues faced by a monopolist.
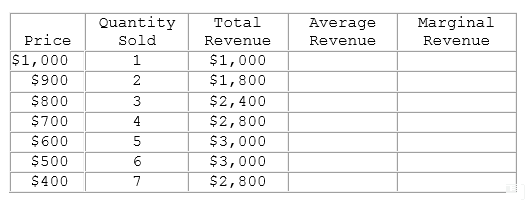
A. increases, then decreases as output increases.
B. is negative after the 6th unit.
C. increases as output increases.
D. decreases, then increases after the 6th unit.
Assume that Dusty has $30 in income, the price of a loaf of bread is $1.50, and the price of a jar of peanut butter is $3. Suppose that at the original income of $30, the price of a loaf of bread increased to $3 and the price of a jar of peanut butter decreased to $2. Dusty can buy a maximum of ________ loaves of bread or a maximum of ________ jars of peanut butter.
A. 20; 15 B. 15; 20 C. 15; 10 D. 10; 15